Electric Vehicles and Barbados
Electric Vehicle Charging
At present, there three different standards of electric vehicle charging are supported by almost all EV manufacturers. While the “charging station” is designed to safely provide power, charging is controlled by the charger in the electric vehicle.

Level 1
Level 1 generally plugs into a standard 120-volt electric wall outlet, and requires up to 12 amps. A portable Level 1 "cord set" comes with most EVs.
One end of the "cord set" plugs into a standard outlet and the other end plugs into the vehicle. The outlet must be a 3-prong, grounded outlet. Many EV drivers charge Level 1 at home. This type of charging can provide about 5 additional miles of EV range for every hour charged.

Level 2
Level 1 generally plugs into a standard 120-volt electric wall outlet, and requires up to 12 amps. A portable Level 1 "cord set" comes with most EVs.
One end of the "cord set" plugs into a standard outlet and the other end plugs into the vehicle. The outlet must be a 3-prong, grounded outlet. Many EV drivers charge Level 1 at home. This type of charging can provide about 5 additional miles of EV range for every hour charged.
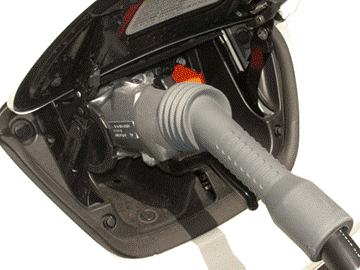
DC Fast Charging
Many BEVs have an inlet for DC fast charging as standard equipment or as an option. The electric vehicle controls the total amount of energy which can be taken in one charge session.
A Nissan Leaf can fast charge from empty to 80 percent in about 30 minutes for the first generation leaf and about 45 minutes for the newer Leafs (assuming a 50 kW DC Fast Charger) . Cost and electrical requirements make fast chargers suitable only for public settings.